Completed Gear
Gear refers to a mechanical element with continuous meshing of gears on the rim to transmit motion and power.
According to the gear structure, it can be divided into gear teeth, cogging, end face, normal face and other parts. Commonly used steels for gear manufacturing include quenched and tempered steel, hardened steel, carburized hardened steel and nitriding steel.
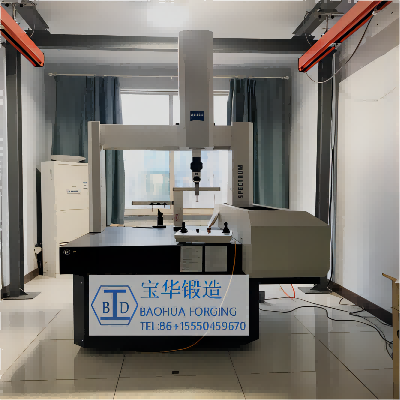
Our company independently designs dies and forges according to product specifications. Material types and weights can be made according to customer requirements. This gear company independently designed the die to achieve precision forging, so that the material utilization rate reaches more than 90%, which greatly saves the cost. Our company also has roughing, heat treatment and finishing, which can be delivered according to customer requirements in different delivery states. About finishing our company has more than 80 sets of different processing machinery and equipment, as well as ZEISS three coordinates, Japanese small plate profilometer, gear tester, Omega tool counter and other inspection and testing equipment.



Gear tooth (tooth) - each convex part of a gear used for meshing. Generally speaking, these bulges are arranged in a radial manner. The teeth on the mating gear are in contact with each other, resulting in the continuous meshing operation of the gear.
Cog space between two adjacent teeth on a gear.
gear
gear
End face the plane perpendicular to the axis of a gear or worm on a cylindrical gear or worm.
Normal plane on a gear, the normal plane is the plane perpendicular to the tooth line of the gear.
Addendum circle the circle in which the top of a tooth is located.
Dedendum circle the circle where the groove bottom is located.
Base circle the circle on which the generating line of an involute forms a pure roll.
Dividing circle - the reference circle for calculating the geometric dimensions of the gear in the end face. For spur gears, the modulus and pressure angle on the dividing circle are standard values.
Tooth surface the side surface of a gear tooth between the top cylindrical surface and the root cylindrical surface.
Tooth profile the section of a tooth surface that is cut by a specified surface (a plane for cylindrical gears).
Tooth line - the intersection line between the tooth surface and the indexing cylinder.
End face pitch pt -- the indexing arc length between the end face tooth profiles on the same side of two adjacent teeth.
Modulus m - the quotient obtained by dividing the pitch by pi, in mm.
Diametral pitch p - reciprocal of modulus, in inches.
Tooth thickness s - the length of indexing arc between the tooth profiles on both sides of a gear tooth on the end face.
Groove width e - the length of the dividing arc between the tooth profiles on both sides of a tooth groove on the end face.
Tooth crest height h ɑ -- The radial distance between the addendum circle and the indexing circle.
Root height h f - the radial distance between the reference circle and the root circle.
Full tooth height h - the radial distance between the addendum circle and the root circle.
Tooth width b - axial dimension of gear teeth.
Welcome to inquiry online.